Here at Orthopedic Surgery San Diego, we offer a comprehensive approach to elbow surgery and elbow pain. Rather than simply focusing on a single point source of patient distress, our advanced imaging and diagnostic tools analyze the full joint for anything amiss. Ligaments, tendons, muscles and bones all play a role in the proper function of the elbow, and even systemic issues such as circulation can play a role. This holistic approach incorporates the full breadth of our understanding of pain and biomechanics.
Dr. Robert Afra is widely renowned as one of the foremost orthopedic surgeons in the nation, and his experience leads an expert team of technicians and medical professionals in every elbow surgery procedure we offer. Our focus is on the total patient, so we consistently exhaust all nonsurgical options before considering a more permanent approach such as elbow surgery. This includes a variety of minimally invasive options such as therapy and non-operative treatment.
If elbow surgery is necessary, we offer a diverse selection of procedures to relieve all major issues, including:
- Lateral epicondylitis
- Medial epicondylitis
- Elbow osteoarthritis
- Osteochondritis dessicans
- Elbow instability
- Cubital tunnel syndrome
The elbow is an intricate and powerful joint that facilitates nearly every advanced motion we humans have evolved to make. From twisting and lifting to basic gestures, the elbow is an essential tool in most people’s active lives. If elbow pain flares up or the joint’s movement is diminished in any way, the consequences can be debilitating. We usually don’t think about our elbows until they hurt, but they are an important part of the body. They allow the hands to side to side and to and from the body. The elbow allows the arms to lengthen and shorten to the space the hand is needed to be at any given time. When we have elbow pain, even something small like lifting a glass or opening a door can be painful. If your elbow is causing pain, it is time to seek medical attention. If you would like to schedule an elbow surgery consultation, please contact us to learn about your options
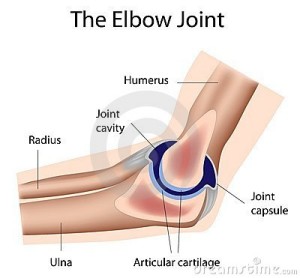
The Elbow
The elbow is a synovia joint, which is a common joint in the body that allows movement. It is also a hinge joint as it only allows movement in one plane (it bends one way only). The elbow is located between the ulna and radius (long bones in the forearm) and the humerus (the long bone in the upper arm). The tip of the elbow is called the olecranon, which is commonly referred to as the “funny bone” (although there’s nothing funny about the pain that occurs when it is bumped). There are three joints in the elbow; the humeroulnar, humeroradial, and superior radioulnar joints. The humeroulnar joint is a hinge joint located at the junction between the ulna and the humerus. It enables the elbow to flex and extend. The humeroradial joint is a ball and socket joint located between the top of the radius to the smooth part of the humerus. The superior radioulnar joint is located at the top of the radius to the notch of the ulna. This allows the arm to be rotated inwards and outward.
Warning Signs of Elbow Injury:
- Pain in elbow
- Pain in elbow that runs to lower or upper arms
- Tenderness in the outside knob of elbow
- Weakness or pain when lifting, making a fist, raising hand
- Swelling or heat of the elbow joint
- Lack of mobility
Elbow conditions can cause pain in the hands, wrist, lower, and upper arms. While home remedies such as rest, splints, or ice may ease the symptoms, elbow conditions still need medical intervention. Lack of proper care can lead to disability and damage. At some point, the Elbow Surgery becomes unavoidable.
Elbow Injuries and Conditions:
- Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)
- Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow)
- Elbow osteoarthritis
- Osteochondritis dissecans
- Elbow instability
- Cubital tunnel syndrome
Lateral Epicondylitis:
Medial Epicondylitis:
Elbow Osteoarthritis:
Osteochondritis Dissecans:
Elbow Instability:
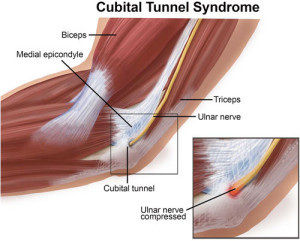
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome:
Elbow Surgery Types
Elbow Arthroscopy
Elbow arthroscopy is a minimally invasive elbow surgery procedure that allows healthcare providers to visualize and treat a wide range of elbow joint problems. With the aid of a small camera called an arthroscope, surgeons can examine the elbow’s intricate anatomy in great detail, enabling precise diagnosis and treatment. Compared to traditional open elbow surgery, elbow arthroscopy offers several advantages, including smaller incisions, reduced pain, and a faster recovery time. This minimally invasive elbow surgery approach effectively alleviates symptoms and restores elbow function, making it a preferred treatment option for various elbow conditions.
Your surgeon may use elbow arthroscopy to:
- Release tensed muscles (contractures).
- Remove loose bone and cartilage.
- Smooth surfaces that contact one another.
- Remove unhealthy tissue or tissue that blocks motion (adhesions).
Total Elbow Arthroplasty
Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) is a surgical elbow surgery procedure that involves replacing the damaged surfaces of the elbow joint with artificial implants. This procedure is typically considered for individuals with severe elbow arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or irreparable fractures that cause significant pain, stiffness, and limited function.
During TEA surgery, the surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone from the ends of the humerus (upper arm bone) and ulna (forearm bone). These surfaces are then resurfaced with artificial components, typically made of metal and plastic, which mimic the natural hinge joint of the elbow.
TEA offers several potential benefits for patients, including:
-
Reduced pain and improved range of motion: By replacing the damaged joint surfaces, TEA can significantly alleviate pain and restore the elbow’s ability to bend and straighten.
-
Enhanced function and quality of life: Improved elbow function allows individuals to perform daily activities more easily, such as dressing, eating, and personal hygiene, leading to an overall improved quality of life.
-
Durability and longevity: Modern TEA implants are designed to be durable and long-lasting, providing relief for years to come.
However, it is important to note that TEA is a major surgical procedure with potential risks and complications, such as infection, loosening of the implant, and nerve damage. Therefore, it is crucial to discuss the risks and benefits thoroughly with an orthopedic surgeon to determine if TEA is the right elbow surgery option for you.
Bicep Tendon Repair
The bicep has two tendons, one attached to the shoulder and the other to the elbow. In Bicep Tendon Repair, a small incision is made in the forearm and a tendon repair device is used to repair and fine-tune the tension on the tendon that is needed for function and mobility. This procedure removes the guesswork from calibrating tendon tension and provides a more efficient repair.
Cubital Tunnel Release
Cubital tunnel release surgery, also known as ulnar nerve decompression, is a surgical procedure that aims to relieve pressure on the ulnar nerve, the nerve that provides sensation and movement to the little finger and half of the ring finger. The ulnar nerve can become compressed or entrapped in the cubital tunnel, a narrow passageway located on the inner side of the elbow, leading to a condition called cubital tunnel syndrome.
Symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome can include:
- Tingling, numbness, or pain in the little finger and half of the ring finger
- Weakness or clumsiness in the hand
- Difficulty gripping objects
Cubital tunnel release surgery involves making an incision in the elbow, releasing the ligaments that compress the ulnar nerve, and providing more space for the nerve to move freely. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and may take about an hour.
After elbow surgery, patients may experience some pain and swelling in the elbow. Ice packs and pain medication can help manage these symptoms. Most patients can resume their normal activities within a few weeks, but it may take several months for the nerve to fully recover.
Cubital tunnel release surgery is a safe and effective treatment for cubital tunnel syndrome. The surgery can relieve symptoms, improve hand function, and prevent further nerve damage.
Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL) Reconstruction:
The ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) is a thick band of tissue that stabilizes the elbow joint and allows for controlled throwing and overhead activities. When the UCL becomes torn or partially torn, it can lead to instability, pain, and a decrease in range of motion. UCL reconstruction, also known as Tommy John surgery, is a common procedure used to repair a torn UCL and restore stability to the elbow.
Indications for UCL Reconstruction
UCL reconstruction is typically recommended for athletes who participate in throwing or overhead sports, such as baseball, softball, tennis, and volleyball, who have experienced a significant UCL tear. It is also sometimes recommended for individuals who experience chronic elbow pain and instability due to a UCL tear.
The UCL Reconstruction Procedure
UCL reconstruction involves replacing the torn UCL with a healthy tendon graft. The graft is typically taken from another part of the patient’s body, such as the hamstring, palmaris longus tendon, or toe extensor tendon. In some cases, a donor tendon may be used.
During the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision over the elbow and removes the torn UCL. The graft tendon is then passed through small tunnels drilled in the ulna and humerus bones. The graft is then secured to the bones, and the incision is closed.
After UCL reconstruction, patients typically wear a brace for several weeks to protect the healing graft. They then begin a rehabilitation program that gradually increases range of motion and strength. Full recovery from UCL reconstruction typically takes 9-12 months.
Success Rates of UCL Reconstruction
UCL reconstruction is a highly successful procedure, with over 90% of patients returning to their previous level of activity. However, there are some potential risks associated with the procedure, such as infection, nerve damage, and stiffness.
What to Expect from Orthopedic Elbow Surgery
The choice of the most suitable elbow surgery option depends on the nature of the elbow issue, its extent, and individual patient factors. Arthroscopic surgery, a minimally invasive approach, proves effective in addressing various elbow problems such as tennis elbow and early-stage elbow arthritis. On the other hand, open procedures like elbow fracture repair or joint replacement tend to be more advantageous for treating elbow fractures or advanced arthritis.
While recovery time and results will vary for each procedure and patient, here is some general information on what to expect from orthopedic elbow surgery:
- After completing surgery, your orthopedic surgeon will place a bandage over your wound and stitches. Your orthopedic surgeon will provide detailed instructions on how to care for your wound and ease any discomfort, such as by icing your arm or taking pain relievers. You may need to wear an elbow splint for around 7-10 days to stabilize your arm as it heals.
- Once you are cleared to remove your splint, you’ll be instructed to start performing exercises designed to increase your elbow strength, flexibility, and mobility. These motions may be painful at first, but they should gradually feel more comfortable as your elbow becomes stronger within approximately 3-6 months.
- After elbow surgery, most patients are able to return to their daily activities in 2-6 weeks and can resume work in 6-12 weeks, with accommodations made if necessary. As for returning to athletic activities, most patients are advised to wait around 4-24 weeks to make sure the operated elbow has healed enough to participate in sports without a high risk of re-injury.
The majority of elbow surgery patients report a significant improvement in their symptoms, with minimized pain and greater mobility typically achieved six months to one year after surgery. Keep in mind that your personal experience will ultimately depend on your body’s healing rate, the type of surgery you undergo, how closely you follow post-operative instructions and other individual factors.
You can depend on Dr. Robert Afra for Elbow Surgery in San Diego
If you are experiencing ongoing elbow discomfort, it may be time to explore treatment options with an orthopedic specialist such as Dr. Robert Afra in San Diego, CA. A trusted physician in your journey to holistic health. His impressive credentials, coupled with an excellent bedside manner make him one of the leading figures in San Diego sports medicine orthopedic surgery milieu. Having previously served as Chief of Sports Medicine at UCSD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dr. Afra not only navigates the world of orthopedic medicine but also focuses on the whole body – holistic approach.









